
India is witnessing a dramatic rise in allergic disorders, with conditions such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, anaphylaxis, food and drug allergies, urticaria, eczema, and angioedema affecting an increasing proportion of the population. Rapid urbanization, environmental pollution, changing dietary habits, and stress have significantly altered the immune landscape, making allergies a common health concern. Estimates suggest that 20-30% of India’s population now suffers from at least one allergic condition, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive and sustainable management strategies.
While modern medicine provides symptomatic relief through antihistamines, corticosteroids, and immunotherapy, Ayurveda offers a holistic, root-cause-oriented approach that not only alleviates symptoms but also enhances immune resilience. This approach is particularly valuable in allergic conditions affecting multiple systems, including the respiratory system, skin, and eyes, where Ayurvedic interventions aim to modulate the immune response and restore physiological balance.
Bala and Vyadhikshamatvam
Modern immunology categorizes the body’s defense system into innate immunity, an immediate non-specific response, and adaptive immunity, which evolves through exposure to pathogens or immunization. Ayurveda, however, conceptualizes immunity as Bala (vitality and strength), a fundamental determinant of disease resistance.
Acharya Charaka, in the Charaka Samhita (Sutrasthana), classifies Bala into three types: Sahaja Bala, the innate strength one is born with, akin to genetic immunity; Kalaja Bala, influenced by age and seasonal variations, recognizing that immunity fluctuates over time; and Yukthikrita Bala, derived from lifestyle, diet, and conscious health practices, aligning with adaptive immunity and immune modulation.
Beyond Bala, Ayurveda introduces the concept of Vyadhikshamatvam, which embodies two key principles: Vyadhi Utpada Pratibandhakatvam, the body’s ability to prevent disease onset, and Vyadhi Bala Virodhitvam, the strength to mitigate the severity of an existing illness. These principles are particularly relevant in allergy management, where an overactive immune response leads to hypersensitivity reactions such as wheezing in asthma, itching in eczema, or ocular irritation in allergic conjunctivitis. Ayurveda’s emphasis on enhancing natural resistance rather than simply suppressing symptoms makes it a unique and sustainable approach to allergy management.
The Role of Dosha Imbalance and Agni Dysfunction
Ayurveda views allergies as systemic imbalances triggered by dietary, lifestyle, and environmental factors that disrupt Agni (digestive fire) and create Ama (toxic metabolic byproducts). This dysfunction weakens Rasa (plasma) and Rakta (blood), impairing immune function and tissue nourishment, ultimately leading to allergic manifestations.
The Ayurvedic understanding of allergy pathogenesis, or Samprapthi, classifies allergic triggers into four major categories:
1. Aharaja (Dietary Triggers) – Consumption of incompatible foods, such as dairy and seafood together, or excessive intake of cold, heavy, and processed foods, disrupts digestion and accumulates Ama, leading to Kapha-related congestion and hypersensitivity reactions.
2. Viharaja (Lifestyle Factors) – Exposure to environmental pollutants, excessive screen time, or chronic sleep deprivation weakens the body's ability to adapt, particularly affecting Vata and Pitta dosha, manifesting as allergic rhinitis, skin inflammation, or ocular irritation.
3. Manasika (Mind-Body Connection) – Emotional stress, anxiety, or suppressed emotions contribute to allergic conditions by disturbing Vata and Pitta, leading to flare-ups of conditions like eczema, urticaria, or tension-related ocular allergies.
4. Agantuja (External Allergens) – Dust, pollen, pet dander, smoke, and chemical irritants act as Agantuja (external) factors, triggering an exaggerated immune response, resulting in seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, sinusitis, and respiratory allergies.
By identifying the root cause of an allergic condition, Ayurveda customizes treatment to address dosha imbalances, enhance Agni (digestive strength), and eliminate Ama, thereby strengthening Vyadhikshamatvam (immune tolerance) and reducing allergic hypersensitivity.
Ayurvedic Immunomodulation:
Ayurveda employs a threefold therapeutic approach to modulate immune function, detoxify the body, and restore balance:
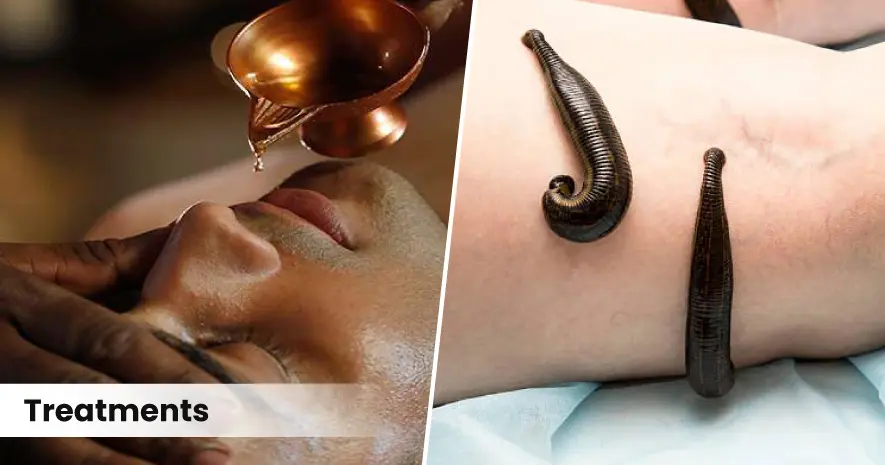

1. Shodhana Chikitsa (Purification Therapy) to Detoxify the System
Purification therapies, known as Panchakarma, help expel accumulated Doshas, cleanse bodily channels (Srotas), and regulate immune responses. These include:
- Vamana (Therapeutic Emesis) : Beneficial in respiratory allergies, this therapy clears Kapha accumulation in the lungs and sinuses, reducing congestion, sinusitis, and allergic conjunctivitis.
- Virechana (Purgation Therapy) : Aimed at detoxifying Pitta dosha, this process clears inflammatory toxins from the blood, reducing eczema, urticaria, and ocular inflammation.
- Nasya (Nasal Instillation Therapy) : The administration of medicated oils or herbal extracts into the nostrils clears the nasal passages and sinuses, providing relief from allergic rhinitis, congestion, and eye irritation due to airborne allergens.
- Rakta Mokshana (Blood Purification Therapy) : Used in chronic skin allergies and inflammatory conditions, this technique helps remove toxins from the bloodstream, reducing hypersensitivity and immune overreaction.
Scientific studies suggest that Panchakarma therapies reduce inflammatory markers and improve immune homeostasis, making them valuable in allergy management.
2. Shamana Chikitsa (Pacification Therapy)
Following detoxification, Ayurveda employs herbal medicines that have anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, and immune-modulatory properties. Turmeric (Curcuma longa) and Ginger (Zingiber officinale) act as natural mast cell stabilizers, reducing histamine release and allergic inflammation. Neem (Azadirachta indica) and Amalaki (Emblica officinalis) detoxify the blood and enhance immune regulation, offering relief from skin allergies and eye irritation.
Recent pharmacological studies validate these herbs’ anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects, demonstrating their ability to regulate Th2-mediated hypersensitivity responses common in allergic disorders.
3. Rasayana Chikitsa (Rejuvenation Therapy)
Rejuvenation therapy plays a crucial role in long-term allergy prevention, strengthening Ojas (vital energy) and enhancing immune resilience. Adaptogenic herbs like Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) and Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus) reduce stress-induced allergic flares, while Triphala (a blend of three fruits) enhances ocular health, reducing eye strain and allergic conjunctivitis.
Modern research highlights Rasayana herbs' role in modulating cytokine levels, enhancing T-cell function, and stabilizing mast cells, which are pivotal in allergic responses. This aligns Ayurvedic rejuvenation therapies with modern immunotherapy, reinforcing their potential in allergy prevention.
Ayurvedic Prevention Strategies:
Ayurveda emphasizes preventive care through seasonal detoxification (Ritu Shodhana), lifestyle regulation (Dinacharya), and personalized diet (Pathya). Daily practices such as oil-pulling, herbal eyewashes, and nasal cleansing with Anu Taila help protect the body from environmental allergens. Seasonal adjustments—such as consuming warming foods in winter to counter Kapha buildup and cooling foods in summer to balance Pitta-related inflammation—further enhance immune adaptation.
By avoiding allergenic triggers, strengthening digestion, and regulating stress, Ayurveda prepares the immune system to handle allergens effectively, reducing the severity and frequency of allergic reactions.
As allergic diseases continue to rise, an integrative approach that combines modern pharmacotherapy with Ayurvedic immune modulation offers a promising pathway for long-term relief and holistic well-being. Ayurveda’s individualized, preventive, and curative framework empowers individuals to fortify their immune system naturally, making it a valuable complement to conventional treatments. By adopting Ayurveda’s principles of balance, detoxification, and rejuvenation, individuals can achieve sustainable allergy control, enhanced vitality, and overall systemic harmony.

March 05, 2026

February 11, 2026

February 11, 2026

January 29, 2026

January 23, 2026
January 12, 2026
We use cookies that are necessary for the smooth operation of the website, to improve our website and to display advertising relevant to you on social media platforms and partner websites. By clicking "Accept all", you agree to the use of cookies for convenience features and statistics and tracking. You can change these settings again at any time. If you do not agree, we will limit ourselves to technically necessary cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .